|
|
For managing, manipulating and mapping GPS data |
|
Description Versions GPS Receivers Features Function List Download Registration Things to Do
Conditions of Use
User Group
Home Description Versions GPS Receivers Features Function List Download Registration Things to Do
Conditions of Use
User Group

Home Description Versions GPS Receivers Features Function List Download Registration Things to Do
Conditions of Use
User Group

Home Description Versions GPS Receivers Features Function List Download Registration Things to Do
|
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
How do I test my communication port?Do the following steps:
My GPS has a serial cable interface, but my computer only has USB ports.To connect a GPS with a serial cable to a computer which only has USB ports you need to obtain a USB/Serial cable adapter, such as the "USB-Serial Cable Adapter" available from www.pfranc.com. The cable comes with a software driver which you must install first. When you plug the cable into a USB socket on your computer, the software creates a virtual serial port within the computer to which GPSU can connect. Connect you GPS via its own serial cable to the adapter cable. In GPSU, use the 'Check' button in the GPS|Setup.. dialog. This will tell which serial port numbers are available. Select that port which appears when you plug in the cable. As an alternative to using the Check button, go to the Control Panel -> Performance and Maintenance -> System ->Hardware -> Device Manger -> Ports to see which virtual serial port your software has generated. Use this port number in GPSU|Setup... It is possible that the port number may change on different bootups so you may need to check this. In some cases it is not wise to boot-up the computer with the USB/Serial cable attached, as then the operating system may decide it is a mouse and not a GPS. Bootup first and THEN plug the cable in - that is once the operating system has completed its powerup sequencing and already found the mouse. The coordinates in GPS Utility differ from GPS values.
|
|
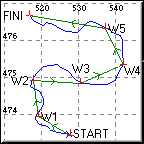
Tracks may show the detailed path between 2 waypoints, whilst a Route only shows the straight line path between 2 waypoints.
Warning: When a route is shown graphically by lines connecting the waypoints, the lines DO NOT INDICATE that the ground path actually follows a straight line. The connecting line only implies that two waypoints are sequential. Whilst a straight line indicates the general direction 'a bird would fly' between waypoints it may NOT BE SAFE TO FOLLOW THE LINE ON THE GROUND.
How can I upload maps to my Garmin receiver?
It is not possible to upload scanned image maps to a Garmin receiver.
Garmin software can upload vector maps (i.e. those consisting of drawn lines). However, Garmin have not published the interface protocol for uploading vector maps and so this function is not supported in GPS Utility.
The best you can do with GPS Utility is to create tracks which can be used as 'pseudo maps'. You can do this by digitising tracks using scanned maps - see the Help topics 'mapping' and 'digitising'. The maps are a bit crude, but it does work for some purposes.
Can I use GPS Utility to delete waypoints in my GPS?
Sorry, it is not possible to delete individual waypoints in your GPS from a PC. The workaround is to download all the waypoints, delete those you do not need, clear all waypoints in your GPS receiver and then upload those that you want to keep.
What is Selective Availability?
Selective Availability (SA) is NO MORE!As of midnight on the 1st May 2000, SA was discontinued under orders of the President Clinton. Selective Availability was the purposeful degradation of the GPS signal for civilian users. This took the form of a timing 'jitter' in the signals coming from the satellites giving a slightly erroneous position (up to 100m for 95% of the time). The military could decode the signal correctly and remove the jitter. Without SA the error is about 15m horizontally and 25m vertically for 95% of the time.
I cannot import the 'intermediate' waypoints from AutoRoute Express / Streets and Trips.
The intermediate waypoints displayed in AutoRoute Express or Streets and Trips are NOT exported in the file - they are obtained when needed from the CD data base which is encrypted. Therefore they cannot be imported into GPS Utility.
If you want intermediate route waypoints, then you need to define them as 'Stop' or 'Via' points first. These are exported and can be read by GPS Utility into a route.
If you also capture the AutoRoute Express/Streets and Trips screen image, then you can calibrate this map image using your Start and End points and then you can quickly digitise the route as a track ready for upload to your GPS receiver. More information regarding this technique is available in Hints and Tips.
I cannot transfer data from 'Discovery Walking Guides' PNF CD to my GPS.
The "Personal Navigator Files" (PNF) files published by Discover Walking Guides contain only waypoint files (*.wpt) and track files (*.plt). The files do not contain any routes (in the Garmin or Magellan sense of this term).The DWG PNF *.wpt files contain a set of waypoints which are in the correct route order. If you want to make a route in GPSU, then open the *.wpt file and check that the waypoints look right in the waypoint table view and in the map view. Do 'Record|Select All' and then 'Tools|Insert in Route'. From the Insert waypoint in Route dialog, select an empty route using the up/down arrow keys and then 'All'. Note: it is best not to choose Route 00. This will create a Route which you can see in the Route table view. Please note the warning shown in red regarding following routes in the Help topic in GPSU on 'Routes'.
The Freeware version of GPSU is limited to 5 Routes, each of a maximum of 10 waypoints per route. See the Help topic in GPSU on 'freeware' for details.
In GPSU if you open a *.plt file then it appears in the track table. However, the *.plt files may not have a track name and when such a file is opened in GPSU the track name is empty. Many Garmin GPSs REQUIRE that all tracks are named. To do this in GPSU go to the track summary table and double click on the track, then enter a name in the dialog.
Also see the Help topic in GPSU on 'Garmin Notes'->Tracks.
Please note that this these are limitations of the PNF files and are not a shortcoming of GPSU.
I upload waypoints to my Garmin but they do not appear to be there in the GPS.
When you upload waypoints to a Garmin they may not be visible in the waypoint table. This is usually because you have the Garmin waypoint find mode set to "Find by Nearest". In this mode, waypoints which are located some distance away from the current (or last known) position fix, will not be displayed.Change the waypoint find mode to "Find by Name" and you should see them. - go to the Waypoint MENU to change the mode and/or check your manual on how to do this.
I get an error on uploading Routes to my Magellan.
When uploading a Route to a Magellan, if you get an error message similar to "Unable to load record. $PMGRTE ......", then this usually means you are trying to load a Route with more waypoints than the Magellan will accept. In some Magellan GPS receivers (e.g. 315, Explorer and SportTrack), the receiver then goes into a permanent error state which is difficult to clear (this is a bug in the Magellan GPS).Usually the only way to clear it is to delete ALL routes in the Magellan and then try reloading the data. When you reload the data ENSURE that all routes do not contain more waypoints than is acceptable to the GPS (usually 30 waypoints).
When I download Waypoints from a Magellan 315, the download stops after a few waypoints.
Sometimes waypoints may become corrupted in a Magellan 315 and the only way to download them is to delete them in the Magellan itself.For example, you may be able to download 8 waypoints OK and then an error occurs. In this case, try deleting the 9th waypoint in the Magellan and try again. This way you may get more waypoints next time. Alternatively, save the 8 waypoints you have already downloaded in a file and then delete those from the 315 and try for more. Hopefully in this way you will be able to recover most of your uncorrupted waypoints. If you manage to get all your waypoints downloaded, then do a memory reset in the Magellan 315 - clear memory of all routes and waypoints and then upload the waypoints again.
I have some data which is referenced to the wrong datum. How can I correct this?
To correct the data you need to 'fool' GPSU into accepting it with a different datum definition.Open your file of data in GPSU. If not a GPSU file then save it in its current datum. Now switch the datum in GPSU to the correct datum and save the file again. You will now have 2 GPSU format files one in each datum. Open both files using a standard text editor and swap the 2 datum definition lines (the Lines beginning with 'M E'). between the files. Save the files from the text editor and then open in GPSU. One file will now be corrected and the other file will be twice as wrong. Discard the wrong file and keep the corrected file.
How do I get my Garmin Nuvi, Colorado, Oregon, Zumo or Edge705 to work with GPSU?
The Garmin Nuvi, Colorado, Oregon, Zumo and Edge 705 models do not support transfer of data via the PC interface as other Garmin models. Instead they behave as a removable media USB Mass storage device via the USB interface. To transfer data from/to these Garmin models, you use File|Open.... and File|SaveAs... and navigate to the folder containing the GPX files. When saving data, save as an *.gpx file (GPS Interchange file). See your Garmin manual regarding this.